Schroder ISF Global Credit Income
Blending the right mix for changing investment climatesWhy global credit income
Late cycle environment
De-synchronization of sector and issuer performance creates opportunities

Low growth
Investors should consider global credit as one of the higher yielding alternatives compared to Sovereigns
Increased volatility
Market volatility is here to stay which requires a more dynamic management approach

Downside risk remains
Focus on balancing return and potential downside risk as volatility persists
Key attributes of the fund
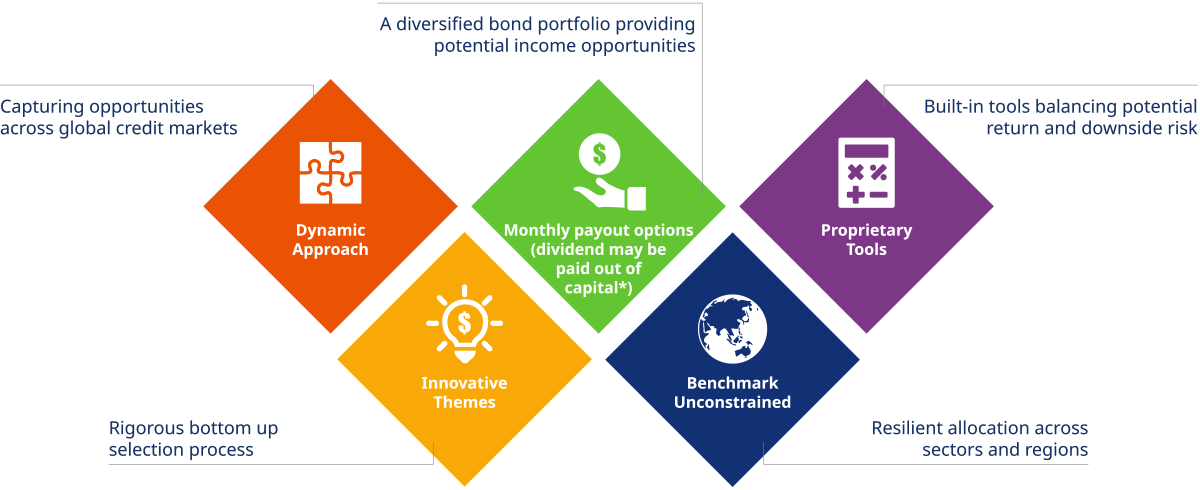
Think Income. Think Stability. Think Innovation.
Think Income
Flexibility in investing across a wide range of bonds and credits
Invest freely across the global bond spectrum.
The fund is managed with a benchmark unconstrained approach, we can invest across sectors and regions to capture attractive income opportunities and to help mitigating risk by diversification.
Providing monthly and fixed payout choices
(dividend may be paid out of capital)*
Bonds are popular investments for income seekers. In the current interest rate environment, which may remain high for a period of time, a portfolio composed of various types of bonds could enhance potential returns with a sensible balance of risks. The fund’s primary target is to maintain sustainable and attractive payment, and intends to make a fixed payout of 6.5% p.a. (Applicable to A Dis MF USD and HKD classes)*
*For distribution share classes/units, the distribution rate is not guaranteed. Distribution yield is not indicative of the return of the fund. Distributions maybe paid out of the capital of the fund at the Manager’s discretion. This amounts to a return or withdrawal of part of the amount you originally invested or capital gains attributable to that and may result in an immediate decrease in the net asset value per share or decrease in the value of units of the relevant Distribution Units.
The manager will make distributions in respect of distribution units. The manager has the sole and absolute discretion to vary the rate and/or frequency of distributions, subject to one month’s prior notice to the relevant unitholders. Distribution yield is not indicative of the return of the fund. Distributions may be paid from capital of the fund. Investors should note that where the payment of distributions are paid out of capital, this represents and amounts to a return or withdrawal of part of the amount you originally invested or capital gains attributable to that and may result in an immediate decrease in the value of units. For details of the distribution policy and frequency of all share classes, please refer to the Distribution calendar and policy.
Think Stability
Rigorous risk management to mitigate volatility
We recognise that income seekers can be more sensitive to capital loss. A well-diversified bond portfolio built under dynamic asset allocation allows the fund to reduce risk in market downturns. Detailed downside risk analysis as well as management on currency and interest rate risk are incorporated with an aim to help mitigating potential loss and volatility.
Think Innovation
Innovative themes-based approach
In our credit selection process, we apply forward-looking themes like technological disruption, changing demographics and consumer trends. This approach helps identifying companies that are adapting well to change.
About credit investment
Challenge yourself to see how much you know about credit investment by going thru the different levels of questions
Related documents
Schroder ISF Global Credit Income
You can find more information on the fund including literature and performance data on our fund centre.
Schroder International Selection Fund is referred to as Schroder ISF.
The fund has environmental and/or social characteristics within the meaning of Article 8 of Regulation (EU) 2019/2088 on Sustainability-related Disclosures in the Financial Services Sector (the “SFDR”).
Images are for illustrative purposes only.